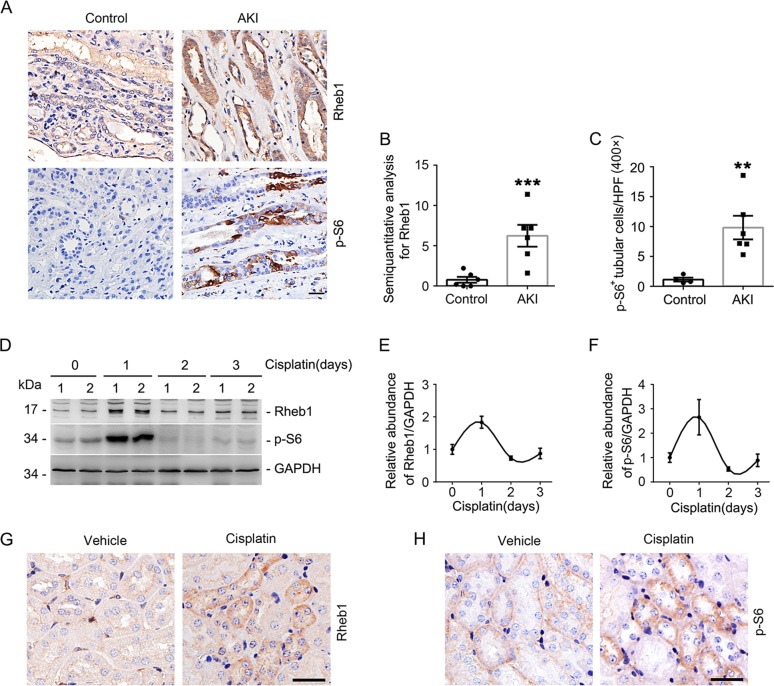
Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb1), a small GTPase, plays an important role in regulating cell growth, differentiation, and survival. However, the role and mechanism Rheb1 in tubular cell survival and acute kidney injury (AKI) is still unexplored. Here we find that Rheb1 signal is activated in the kidney tubules AKI patients and cisplatin-treated mice. A mouse model-specific deletion Rheb1 tubules (tubular-Rheb1 – / -) is generated.
Compared with control littermates, tubular-Rheb1 – / – mice phenotypically normal within 2 months after birth but develop a more severe kidney dysfunction, tubular cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis and ferroptosis, mitochondrial defects and less expression of PGC-1α after injection of cisplatin.
In primary cultured tubular cells, Rheb1 ablation exacerbated cisplatin-induced cell death and mitochondrial defects. Furthermore, haploinsufficiency for Tsc1 in tubule cells leading to activation Rheb1 and reduced cisplatin-induced cell death, disability and maternal mitochondria. Together, these studies revealed that Rheb1 can protect against tubular cell death and cisplatin-induced AKI through maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis.
In HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, elevated toll-like receptor 2 immunoexpression may increase the risk of disease-specific mortality.
Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb1), a small GTPase, plays an important role in regulating cell growth, differentiation, and survival. However, the role and mechanism Rheb1 in tubular cell survival and acute kidney injury (AKI) is still unexplored.
Here we find that Rheb1 signal is activated in the kidney tubules AKI patients and cisplatin-treated mice. A mouse model-specific deletion Rheb1 tubules (tubular-Rheb1 – / -) is generated. Compared with control littermates, tubular-Rheb1 – / – mice phenotypically normal within 2 months after birth but develop a more severe kidney dysfunction, tubular cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis and ferroptosis, mitochondrial defects and less expression of PGC-1α after injection of cisplatin.
In primary cultured tubular cells, Rheb1 ablation exacerbated cisplatin-induced cell death and mitochondrial defects. Furthermore, haploinsufficiency for Tsc1 in tubule cells leading to activation Rheb1 and reduced cisplatin-induced cell death, disability and maternal mitochondria. Together, these studies revealed that Rheb1 can protect against tubular cell death and cisplatin-induced AKI through maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis.